The basic science
Hair is mostly composed of a hardened fibrous protein called keratin. Keratin is made up of amino acids and peptide bonds which originate in the hair follicle. These many amino acids and peptide bonds form the polypeptide chains (coils). The polypeptide chains are held together by permanent and temporary bonds inside the cortex layer of the hair.
Polypeptide chain
The Bonds In The Hair
Hair can be naturally curly, wavy or straight. It is held in its natural state by the permanent and temporary bonds. The permanent bonds are broken by chemicals, such as perm solution, and can change from naturally straight to chemically curly. The permanent bonds are called disulphide bonds; you will learn about these on GH14.
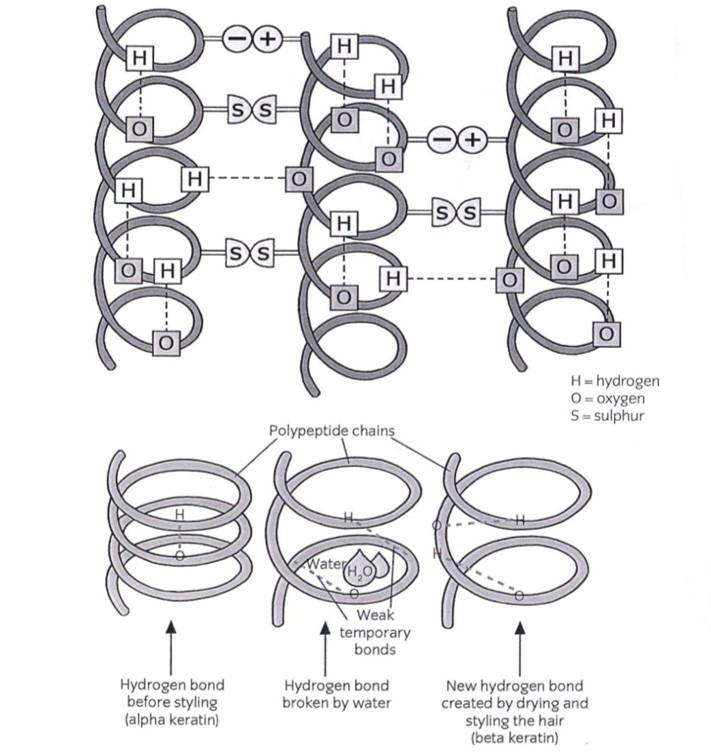
The temporary bonds allow us to temporarily change the natural state of the hair, known as Alpha Keratin, through heat styling. For example curly hair can be washed, stretched and blow-dried straight allowing the natural state of the hair to be temporarily fixed into a new shape, known as Beta Keratin. Wetting the hair through shampooing or humidity in the air will break the temporary bonds again and return the hair to its natural state. The temporary bonds are known as hydrogen and salt bonds. The flow chart below shows what makes up the hair.

Salt Bonds
Salt Bonds are weak bonds that are temporarily softened by changes in PH, by the use of weak acids or alkalis. They are reformed by changing back the PH.
Hydrogen Bonds
The main bonds that are broken when styling the hair are hydrogen bonds. These are broken by water and hardened by drying or cooling the hair. Heat from styling equipment, such as tongs and straightening tongs, can also change the state from alpha keratin to beta keratin – when the hair has cooled into its new shape.
Hydrogen bonds give the hair its strength and its flexibility to move freely; it is what makes the hair elastic. Well conditioned hair with a strong cortex can stretch up to a further half its original length when wet’ this is due to the temporary breaking of the hydrogen bonds.
Alpha and Beta Keratin
Hair in its natural state of curly, wavy or straight is described as being in an alpha keratin state. When hair has been wetted, stretched and dried into a new shape it is described as being in a beta keratin state.